GPRP Diesel

This package is designed for direct injection, common rail, turbo diesel engines, but can also be used for naturally aspirated diesel applications. Many features of MoTeC's petrol GPR packages have been reproduced in this package, providing a familiar feel for current GPR users.
Many auxiliary features commonly found on racing cars are included, such as launch control, traction control, driver switches (e.g., pit switch, launch enable, boost compensation), gearbox control, intercooler sprays, transmission pump, differential pump, and coolant pump. Also accommodated are many systems found on modified road vehicles, such as air conditioning.
The package fully integrates with other MoTeC products and provides predefined CAN messages for all current display loggers, recorders, E888, VCS, GPS, ADR, BR2, PDM and SLM. A vector database file (.dbc) is also available upon request.
Features
The following GPR Diesel features are specifically designed to operate diesel engines:
- Operates 1- to 8-cylinder direct injection diesel engines with inductive or piezoelectric injectors and synchronous direct injection fuel pumps. See section Engine compatibility to obtain the known applicable mechanisms.
- Turbocharger boost pressure control from a PWM solenoid or servo motor for use with a Variable Nozzle Turbo (VNT), Wastegate, Bypass, etc. Boost control is fully configurable via a PID control system giving the user full control over system response and stability. Boost Aim can vary based on fuel mass, engine speed and ambient pressure.
To ensure safe operation, various boost limits can also be set. These limits can be based on coolant temperature, engine load, exhaust temperature, intake air temperature, run time, gear, vehicle speed, and turbocharger speed.
- Control of a throttle valve is also supported. This throttle valve can be used to assist in engine shutdown or reduce power during Engine Run-Over Operation.
- Exhaust gas recirculation control via a servo motor, solenoid or stepper motor actuator. The amount of EGR applied can vary with engine speed and fuel mass. Compensations for air temperature, coolant temperature and ambient pressure can also be applied.
A start-up EGR compensation can be used to prevent soot formation when the vehicle takes off. Separate EGR targets can be used for Overrun and Gear Shifts. The Throttle Servo or a Flap Actuator (EGR Cooler) can also be controlled during EGR requests.
- The glow plug control system includes independent strategies for controlling the glow plugs before starting, during starting and after starting. Each stage has adjustable compensations for coolant temperature and battery voltage.
- Ignition outputs are available for each cylinder to check fuel injection timing.
- Advanced LTC Enable functionality ensures safe operation of Lambda sensors.
Adapter kits for common diesel vehicles will be available soon. These adapter kits connect the vehicle's original engine harness directly to the M1 without the need to modify the existing OE wiring.
The following sensors are required to operate a diesel engine with this GPR Diesel package:
- Coolant temperature sensor
- Direct Fuel Pressure Sensor (Common Rail)
- Mass air flow sensor or intake manifold pressure sensor and intake air temperature sensor (all 3 preferred)
- Accelerator pedal sensor
- Engine speed reference sensor
- Engine timing sensor (camshaft position)
For optimal performance, the following sensors are recommended for use with the GPR Diesel package:
- Exhaust temperature sensor
- Boost pressure sensor
- Fuel temperature sensor
- Ambient pressure sensor
This package is available for use with MoTeC direct injection ECUs: M141 and M142. A package variant for M130 and M150 ECUs is also available and is used in conjunction with an injector drive box fitted to some vehicles (e.g. Toyota Hilux).
The main difference between MoTeC's M141 and M142 ECUs is the maximum available boost voltage and peak/hold currents for direct injector operation. Consequently, the injector power requirements of any engine must be considered when choosing an M1 ECU.
| ECU | Maximum reinforcement stress | Maximum peak current | Maximum holding current |
|---|---|---|---|
| M141 | 188V | 20ONE | 10ONE |
| M142 | 80V | 20ONE | 15ONE |
See section Engine compatibility of this datasheet to determine the correct ECU for the application. Below is a sample pinout for the M142.
GPRP Features
The following features of the MoTeC GPR Package are retained in the GPR Diesel Package:
- Configurable engine timing mode for many common engine types. See section Engine synchronization modes for current details.
- Configurable top dead center for each cylinder allows for odd-firing engines.
- Configurable camshaft control from 1 to 4 cams, plus 1 switched camshaft.
- Physical settings for engine displacement, fuel properties and injector characteristics allow for simplified engine start-up prior to tuning.
- Sensor calibrations are available for many common automotive sensors. Sensor calibrations can also be set manually.
- Support for analog and digital sensors (frequency or duty cycle).
- Support for single-wire digital sensors (SENT).
- Diagnostics on all sensors to check for high and low shorts. When diagnostics detect a fault, the package either disables all functions that use the faulty sensor or uses the sensor's default estimates. The air box mass flow sensor has extra plausibility diagnostics to check for shift and gain faults.
- Support for MoTeC devices: ADR, E8XX, PDM, SLM, Video Systems
- Supports CAN messages for BOSCH ABS M4 unit.
- Test settings for most outputs, including injection and ignition outputs, to make setup easier.
- Configurable turbocharger bypass (blow-off) control.
- Supports two cooling fan outputs (PWM controlled).
- Configurable closed loop alternator control system for PWM field winding control.
- Support for air conditioning with switched output control and optional refrigerant pressure sensor.
- Cooling pump output with PWM control.
- Coolant pump after-run functionality, optionally with additional pump output.
- Engine speed limitation by fuel cutoff.
- Fuel pump switched output.
- Fuel Flow Supply Sensor and Fuel Return Flow Sensor.
- Gearbox position detection via optional dual sensor or engine speed/wheel speed estimation.
- Gearbox shift request via upshift switch/downshift switch or shift lever force sensor.
- GPS acquisition and recording via CAN or RS232.
- Support for GLONASS messages on GPS devices.
- Intercooler temperature and spray control.
- Differential temperature control with dedicated temperature sensor and switched pump output.
- Calculation of the engine load temperature allows correction of the intake air temperature (compensation for the heat absorption effect, etc.).
- Distance, time and lap number via BR2, GPS or switched input, with split and sector options.
- Configurable launch control with tables for engine speed, throttle limit, thrust aiming and fuel volume compensation.
- Race timing system with tables for fuel mass, fuel time, acceleration limit and acceleration limit.
- Engine load average channel with tables for engine speed limit and boost limit.
- Intake Manifold Flap Support (actuator with position).
- Intake manifold support (actuator with position feedback).
- Assisted engine start control with dedicated fuel mass and idle compensations during cranking and subsequent starting.
- Total engine running time for engine hour logging.
- Configurable security for multiple users with different access options.
- Setting the brake state using a switch or pressure sensor.
- Setting the clutch state using a switch, a position sensor or a pressure sensor.
- Transmission brake control ('bump') functionality for perfect positioning of cars, with 'slide' feature.
- Calculation of clutch slip ratio.
- ECU internal G-force (acceleration) – longitudinal, lateral, vertical.
- The ECU CAN receive from a defined CAN ID for receiving data from MoTeC devices.
- Support of up to three separate CAN buses.
- Most common ECU channels transmitted over CAN using standard MoTeC CAN models.
- 8 configurable toggle switches and 8 rotary switches (wired or CAN input) each with 10 positions. They can be simultaneously mapped to Launch Control, Pit Stop, Traction, Race Time Reset, Engine Max Speed Limit, Accelerator Pedal Travel, Boost Limit, Traction Aim and Traction Control Range, Transmission Brake Bump, Wheel Circumference and Wheel Max Speed Limit Switch.
- Pulsed tachometer output with configurable output pin and scale.
- Drive by Wire dual bank throttle servo control.
- Configurable throttle sensor input, with 2-channel analog or single-wire digital (SENT) protocol.
- Accelerator pedal sensor with translation table. Hybrid OE pedals (e.g. Ford) are supported – one analog and one digital channel.
- Use of an accelerator pedal sensor or a throttle position sensor in the case of a cable throttle.
- Differential pump output with user-defined differential temperature control.
- Transmission cooler pump outlet with user definable transmission temperature control.
- Traction control with tables for Aim Main, Aim Compensation and Control Range.
- Measuring vehicle speed using wheel speed sensors, estimation or GPS.
- Vehicle speed limit control system, which can also be used for well speed limitation.
- Configurable warning system with light output and CAN.
- 5 auxiliary output functions for PWM control of actuators added. Output duty cycle control can be varied based on:
- Engine speed and engine load (Output 1)
- Engine speed and accelerator pedal (Output 2)
- Engine Speed and Fuel Mass (Output 3 & 4)
- Motor speed and auxiliary input (output 5)
- Optional channels for additional sensors via input pin and/or CAN message, including:
- Airbox Mass Flow, Mass Flow Reference, Pressure and Temperature
- Ambient pressure and temperature
- Boost pressure
- Front and rear brake pressure
- Brake switch
- Brake vacuum pressure
- Clutch pressure and position
- Clutch switch
- Coolant pressure and temperature
- Differential temperature
- Engine oil pressure and temperature
- Engine crankcase pressure
- Exhaust Pressure Bank 1 and Bank 2
- Exhaust Temperature (EGT) via TCA thermocouple amplifier, generic CAN or E888 for a single manifold, bank 1 and 2 manifolds and cylinders 1 through 8.
- Exhaust lambda via LTC, LTCN or PLM to a single manifold, bank 1 and 2 manifolds and cylinders 1 through 8.
- Fuel pressure and temperature
- Fuel tank level
- Gear position
- Gear lever force
- Gear neutral switch
- Gear change request
- G-force (acceleration) – Longitudinal, Lateral, Vertical
- Inlet air temperature
- Intake manifold pressure and temperature
- Intake manifold flap position x 2, intake manifold runner position
- Intercooler temperature
- Steering angle and pressure
- Transmission pressure and temperature
- Turbocharger speed
- Turbocharger inlet/outlet temperature
- Turbocharger wastegate position
- Front/rear left/right wheel speed sensors, directly wired or CAN input.
Engine Compatibility
Multipulse injection system
Fuel is supplied by up to four pulses: two pilot, one main, and one post-pulse. Fuel mass is calculated as described in the following section, where the total fuel mass can be divided between the pilot and main pulses.
Post pulses are calculated separately from other pulses. They are not considered in terms of torque delivery in an engine, but rather as exhaust treatment or turbo control strategies that have a limited effect on the overall engine torque.
Main pulse system
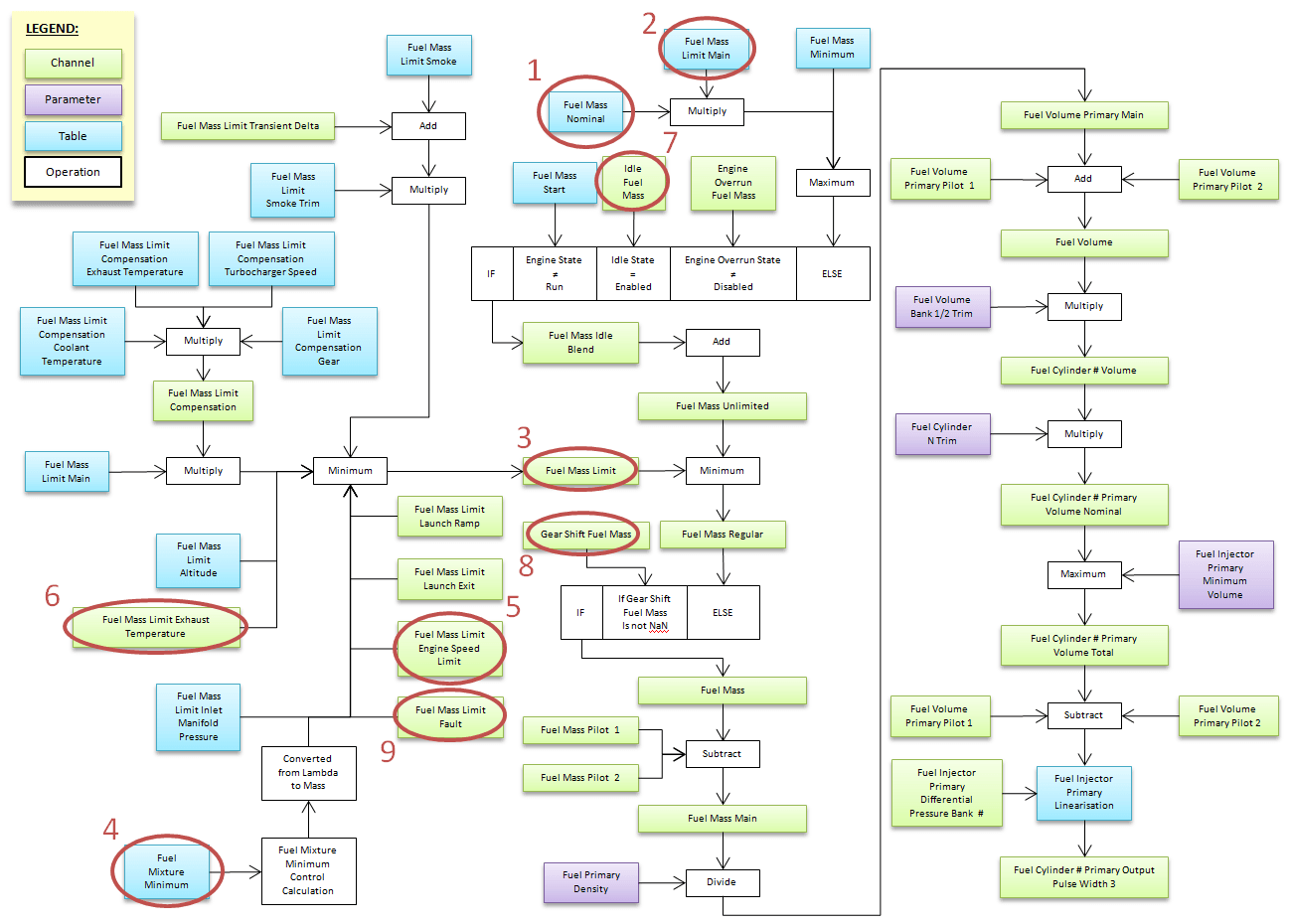
Notice: This section refers to the main injection pulse flowchart on the following page (Fig. 1).
- This package delivers fuel in proportion to the accelerator pedal position (see 1 & 2 in Fig 1, page 1). The fuel mass can then be limited (see 3 in Fig 1) by a series of tables and calculations, including:
- Fuel Mass Limit Smoke
- Fuel Mass Limit Smoke Trim
- Fuel Mass Limit Compensation Coolant Temperature
- Fuel Mass Limit Compensation Exhaust Temperature
- Mass Fuel Limit Compensation Turbocharger Speed
- Fuel Mass Limit Compensation Gear
- Fuel Mass Limit Altitude
- Exhaust temperature fuel mass limit
- Fuel mass limit failure
- Fuel Mass Limit Intake Manifold Pressure
- Minimum fuel mixture
- The Minimum Fuel Mixture Control system applies an adjustment to the Fuel Mass Limit to ensure that the Exhaust Lambda is not richer than the user defined limit, which is set in the Minimum Fuel Mixture table (see 4 in Fig 1).
- The engine speed limitation control system varies the fuel mass to maintain engine speed within user-defined limits (see 5 in Fig. 1).
- Exhaust temperature protection The control system that limits the fuel mass (see 6 in Fig. 1) based on the exhaust temperature can be used to prevent overheating of the exhaust components (i.e. turbocharger).
- Idle speed control with closed loop fuel mass control (see 7 in Fig 1) to ensure smooth and stable engine idle speed. Ramp Down functionality can also be used to provide a smooth transition to idle mode.
- Power-assisted gear changes with independent fuel mass control (see 8 in Fig. 1). Up and down gear changes can be adjusted independently via separate tables.
- Configurable control of up to 2 proportional and 1 synchronous direct injection fuel pumps.
- Fuel mass limits (see 9 in Fig. 1) can be set for each of the 61 individual warnings that can be monitored with the warning system. The warning system determines whether a measurement is outside normal operating conditions or whether a sensor, input or output is defective.
Notices are included for:
- Engine oil pressure
- Engine crankcase pressure
- Direct Fuel Primary Pressure Bank 1 & 2
- Primary fuel pressure
- Coolant temperature
- Inlet air temperature
- Engine oil temperature
- Exhaust lambda
- Exhaust temperature
- Exhaust pressure
- Engine speed
Fig 1: Main injection pulse flowchart
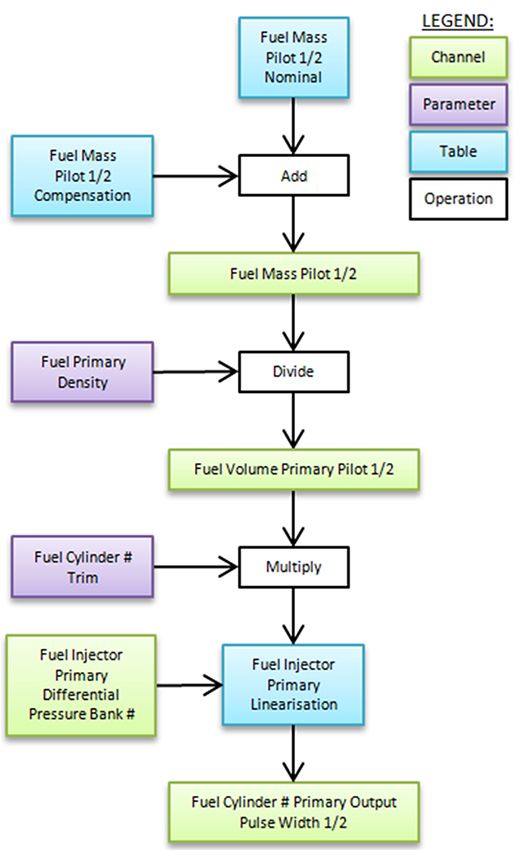
Pilot pulse system
Support for up to two pilot pulses before the main pulse to allow for smoother operation and reduced noise. The fuel mass of each pilot pulse can vary with engine speed and the total mass of fuel being delivered. Pilot fuel mass can also be compensated for coolant temperature. Pilot pulse timing can be relative to TDC, the main pulse, or calculated. Timing can also be varied with engine speed and total fuel mass and can be compensated for coolant and engine load temperature.
Fig 2: Pilot injection pulse flowchart
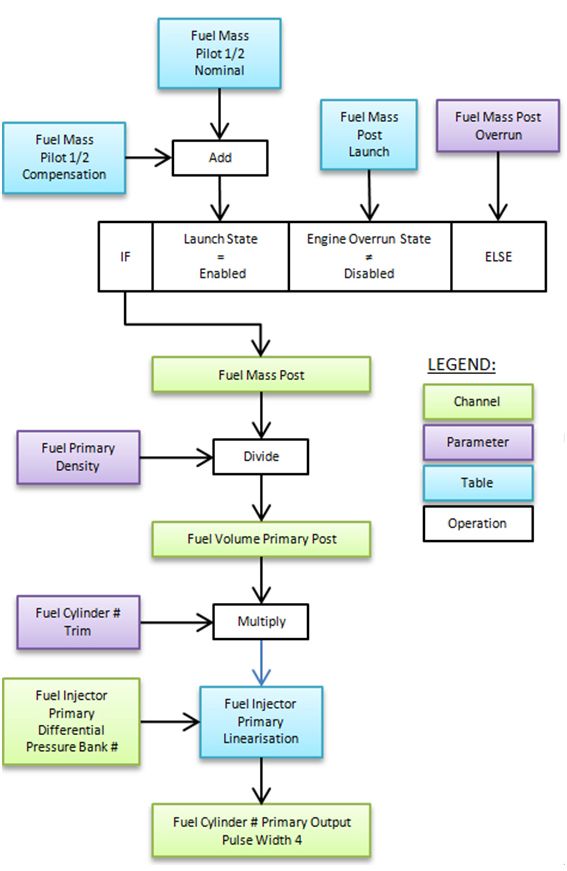
Post-pulse system
A single postpulse after the main pulse can be added to reduce emissions or increase thrust without affecting engine power. The postpulse fuel mass can vary with engine speed and the total mass of fuel being delivered. The pilot fuel mass can also be compensated for by coolant temperature.
Postpulse timing can be relative to TDC, the main pulse or calculated. Timing can also be varied with engine speed and total fuel mass and can be compensated for coolant temperature. Postpulse can be independently controlled at engine coast and launch with options to disable/enable postpulse during gear changes and traction control.
Fig 3: Post-injection pulse flow diagram
Known OE engines that are suitable:
| Engine family | Engine designation | Year | Vehicle platform | ECU | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota KD | 1KD-FTV | 2012-2015 | Hilux KUN16R, KUN26R | M130 or M150*, M141 or M142 | Medium voltage inductive injectors |
| Toyota GD | 1GD-FTV | 2015-2018 | Hilux GUN126R | M141 or M142 | Medium voltage inductive injectors |
| Toyota RV | 1VD-FTV | 2007-2017 | Landcruiser 200 | M130 or M150*, M141 | High voltage inductive injectors |
| Duratorq 3.2 | ZSD Puma (P5AT) | 2011-2018 | Ford Ranger T6 | M141 | Piezo injectors |
| Duratorq 3.2 | MZ-CD 3.2 | 2011-2018 | Mazda BT50 | M141 | Piezo injectors |
| Mitsubishi 4N1 | 4N15 | 2015-2018 | Mitsubishi Triton L200MQ | M141 | High voltage inductive injectors |
| Isuzu J | 4JJ1-TCX | 2012-2018 | Isuzu D-Max | M141 or M142 | Medium voltage inductive injectors |
| GM Duramax | LWN | 2012-2018 | Holden Colorado | M142 | Medium voltage high current inductive injectors |
| VM Motors | R-4028DOHC | 2010-2018 | Jeep Wrangler | M142 | Medium voltage high current inductive injectors |
*The M130 and M150 ECUs can only be used in conjunction with the OE injector drive box.
Engine Rotation Modes
Starting with M1 System 1.4.00.0056
This list only refers to engine modes that are relevant to known diesel engines.
- Bosch 140 40 – General Motors LLT, Audi BXA/Lamborghini LP560, Mazda L3-VDT
- Camshaft one missing four stroke
- Camshaft two missing four strokes
- Crankshaft One Missing Four Strokes
- Crankshaft One Missing Two Strokes
- Crankshaft Two Missing Four Strokes
- Crankshaft Two Missing Two Strokes
- General Motors DMAX LMM – General Motors 6.6L Duramax LMM diesel engines (late 2007 – early 2011) when the eighth digit of the VIN number is 6.
- Isuzu 4JK1
- Mitsubishi Fuso 4P10 (also Agco Sisu Power 49G)
- Mitsubishi Fuso 6M60 – 2015 Fuso TKG-FK61F
- Multi Tooth Four Stroke
- Multi Tooth Two Stroke
- Nissan YS23DDT – Diesel Navara
- Scania DC16
- Scania SGL12A
- Toyota 1GD FTV – 2.8L common rail diesel (2015 – )
- Toyota 1KD FTV – 3.0L common rail diesel (2000 – )
- Volvo D11C – D11C truck engine (FM450 Platform)
Pinout Example
M142 A connector – 34 ways
Mating connector: Tyco Superseal 34 Position Keying 2 – MoTeC # 65067| Pin | Designation | Full name | OE pin | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | AT5 | Analog Temperature Input 5 | Exhaust temperature sensor | |
| A02 | AT6 | Analog temperature input 6 | Coolant temperature sensor | |
| Answer A03 | AV15 | Analog voltage input 15 | ||
| A04 | AV16 | Analog voltage input 16 | ||
| A05 | AV17 | Analog voltage input 17 | ||
| A06 | INJ_D1A_NEG | Direct Injector 1A – | Fuel Cylinder 1 Primary Outlet – | |
| A07 | INJ_D1A_POS | Direct Injector 1A + | Fuel Cylinder 1 Primary Outlet + | |
| A08 | INJ_D1B_POS | Direct Injector 1B+ | Fuel Cylinder 4 Primary Outlet + | |
| A09 | INJ_D1B_NEG | Direct Injector 1B – | Fuel Cylinder 4 Primary Outlet – | |
| Answer 10 | SEN_5V0_C1 | 5.0VC Sensor | ||
| Answer 11 | LA_NB1 | Lambda narrow input 1 | ||
| Answer 12 | LA_NB2 | Lambda 2 Narrow Entry | ||
| Answer 13 | BEAT 3 | Detonation input 3 | ||
| Answer 14 | BEAT 4 | Detonation input 4 | ||
| Answer 15 | DIG2 | Digital input 2 | ||
| Answer 16 | DIG3 | Digital input 3 | ||
| Answer 17 | DIG4 | Digital input 4 | ||
| Answer 18 | SEN_5V0_C2 | 5.0VC Sensor | ||
| A19 | SEN_5V0_B2 | 5.0VB Sensor | 5V analog signal sensor | |
| Answer 20 | LIN | LIN Bus | ||
| A21 | RS232_RX | RS232 Receive | ||
| ANSWER 22 | RS232_TX | RS232 transmission | ||
| A23 | DIG1 | Digital input 1 | ||
| A24 | BAT_NEG3 | Negative Battery | Floor | |
| A25 | BAT_NEG4 | Negative Battery | Floor | |
| A26 | SEN_0V_C1 | Sensor 0V C | ||
| A27 | SEN_0V_C2 | Sensor 0V C | ||
| A28 | CAN3_HI | CAN Bus 3 High | ||
| A29 | CAN3_LO | CAN Bus 3 Low | ||
| Answer 30 | CAN2_HI | CAN Bus 2 High | ||
| A31 | CAN2_LO | CAN Bus 2 Low | ||
| A32 | BAT_NEG5 | Negative Battery | Floor | |
| A33 | SEN_0V_B1 | Sensor 0V B | ||
| Answer 34 | SEN_0V_A1 | Sensor 0V A |
M142 Connector B – 26-way
Mating connector: Tyco Superseal 26 Position Keying 3 – MoTeC # 65068| Pin | Designation | Full name | OE pin | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B01 | OUT_HB9 | Half bridge exit 9 | EGR actuator servo motor – | |
| B02 | OUT_HB10 | Half bridge exit 10 | EGR actuator servo motor + | |
| B03 | UDIG8 | Universal digital input 8 | ||
| B04 | UDIG9 | Universal Digital Input 9 | ||
| B05 | UDIG10 | Universal Digital Input 10 | Engine running switch | |
| B06 | UDIG11 | Universal Digital Input 11 | Air box mass flow sensor | |
| B07 | UDIG12 | Universal digital input 12 | Boost servo actuator position sensor | |
| B08 | INJ_LS5 | Low Side Injector 5 | ||
| B09 | INJ_LS3 | Low Side Injector 3 | ||
| B10 | AV9 | Analog voltage input 9 | Direct Primary Fuel Pressure Bank 1 | |
| B11 | AV10 | Analog voltage input 10 | ||
| B12 | AV11 | Analog voltage input 11 | Engine oil pressure sensor | |
| B13 | BAT_POS2 | Positive Battery | ECU battery voltage | |
| B14 | INJ_LS6 | Low Side Injector 6 | ||
| B15 | INJ_LS4 | Low Side Injector 4 | ECU Power Relay | |
| B16 | AV12 | Analog voltage input 12 | ||
| B17 | AV13 | Analog voltage input 13 | ||
| B18 | AV14 | Analog voltage input 14 | ||
| B19 | BAT_POS3 | Positive Battery | ECU battery voltage | |
| B20 | OUT_HB7 | Half bridge exit 7 | Throttle Servo Bank Motor 1 – | |
| B21 | OUT_HB8 | Half bridge exit 8 | Throttle Servo Bank 1 Motor + | |
| B22 | INJ_D2A_NEG | Direct Injector 2A – | Fuel Cylinder 2 Primary Outlet – | |
| B23 | INJ_D2A_POS | Direct Injector 2A + | Fuel Cylinder 2 Primary Outlet + | |
| B24 | INJ_D2B_POS | Direct Injector 2B+ | ||
| B25 | INJ_D2B_NEG | Direct Injector 2B – | ||
| B26 | SEN_5V0_A2 | 5.0VA Sensor |
M142 Connector C – 34 ways
Mating Connector C: Tyco Superseal 34 Position Keying 1 – MoTeC # 65044| Pin | Designation | Full name | OE pin | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C01 | OUT_HB2 | Half bridge exit 2 | Primary Fuel Pressure Direct Bank Pump 1 + | |
| C02 | SEN_5V0_A1 | 5.0VA Sensor | ||
| C03 | IGN_LS1 | Low side ignition 1 | ||
| C04 | IGN_LS2 | Low Side Ignition 2 | ||
| C05 | IGN_LS3 | Low side ignition 3 | ||
| C06 | IGN_LS4 | Low side ignition 4 | ||
| C07 | IGN_LS5 | Low side ignition 5 | Ignition cylinder 1 (timing light output) | |
| C08 | IGN_LS6 | Low side ignition 6 | ||
| C09 | SEN_5V0_B1 | 5.0VB Sensor | 5V analog signal sensor | |
| C10 | BAT_NEG1 | Negative Battery | Floor | |
| C11 | BAT_NEG2 | Negative Battery | Floor | |
| C12 | IGN_LS7 | Low Side Ignition 7 | ||
| C13 | IGN_LS8 | Low side ignition 8 | ||
| C14 | AV1 | Analog voltage input 1 | Main accelerator pedal sensor | |
| C15 | AV2 | Analog voltage input 2 | Accelerator pedal sensor tracking | |
| C16 | AV3 | Analog voltage input 3 | ||
| C17 | AV4 | Analog voltage input 4 | ||
| C18 | OUT_HB1 | Half bridge exit 1 | Primary Fuel Pressure Direct Bank Pump 1 – | |
| C19 | INJ_D3A_POS | Direct Injector 3A + | Fuel Cylinder 3 Primary Outlet + | |
| C20 | INJ_D3B_POS | Direct Injector 3B+ | ||
| C21 | INJ_D4A_POS | Direct Injector 4A + | ||
| C22 | INJ_D4B_POS | Direct Injector 4B+ | ||
| C23 | INJ_LS1 | Low Side Injector 1 | ||
| C24 | INJ_LS2 | Low Side Injector 2 | ||
| C25 | AV5 | Analog voltage input 5 | ||
| C26 | BAT_POS1 | Positive Battery | ECU battery voltage | |
| C27 | INJ_D3A_NEG | Direct Injector 3A – | Fuel Cylinder 3 Primary Outlet – | |
| C28 | INJ_D3B_NEG | Direct Injector 3B – | ||
| C29 | INJ_D4A_NEG | Direct Injector 4A – | ||
| C30 | INJ_D4B_NEG | Direct Injector 4B – | ||
| C31 | OUT_HB3 | Half bridge exit 3 | Primary Fuel Pump | |
| C32 | OUT_HB4 | Half bridge exit 4 | ||
| C33 | OUT_HB5 | Half bridge exit 5 | Boost Servo Actuator Motor – | |
| C34 | OUT_HB6 | Half bridge exit 6 | Boost + Servo Actuator Motor |
M142 Connector D – 26 Ways
Coupling Connector D: Tyco Superseal 26 Position Keying 1 – MoTeC #65045| Pin | Designation | Full name | OE pin | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D01 | UDIG1 | Universal digital input 1 | Engine speed sensor | |
| D02 | UDIG2 | Universal digital input 2 | Intake camshaft position sensor | |
| D03 | AT1 | Analog temperature input 1 | ||
| D04 | AT2 | Analog temperature input 2 | Intake air temperature sensor | |
| D05 | AT3 | Analog Temperature Input 3 | Primary fuel temperature sensor | |
| D06 | AT4 | Analog temperature input 4 | ||
| D07 | BEAT 1 | Detonation input 1 | ||
| D08 | UDIG3 | Universal Digital Input 3 | ||
| D09 | UDIG4 | Universal digital input 4 | ||
| D10 | UDIG5 | Universal Digital Input 5 | ||
| D11 | UDIG6 | Universal Digital Input 6 | Throttle servo bank 1 position sensor | |
| D12 | BAT_BAK | Battery Backup | ||
| D13 | BEAT 2 | Detonation input 2 | ||
| D14 | UDIG7 | Universal digital input 7 | ||
| D15 | SEN_0V_A2 | Sensor 0V A | 0V sensor for digital signals | |
| D16 | SEN_0V_B2 | Sensor 0V B | 0V sensor for digital signals | |
| D17 | CAN1_HI | CAN Bus 1 High | MoTeC 1 Mbit/sec CAN | |
| D18 | CAN1_LO | CAN Bus 1 Low | MoTeC 1 Mbit/sec CAN | |
| D19 | SEN_6V3 | 6.3V Sensor | ||
| D20 | AV6 | Analog voltage input 6 | EGR actuator servo position sensor | |
| D21 | AV7 | Analog voltage input 7 | ||
| D22 | AV8 | Analog voltage input 8 | Intake manifold pressure sensor | |
| D23 | ETH_TX+ | Ethernet Transmission + | Green/White Ethernet | |
| D24 | ETH_TX- | Ethernet Transmission – | Green Ethernet | |
| D25 | ETH_RX+ | Ethernet + Reception | Orange/White Ethernet | |
| D26 | ETH_RX- | Ethernet Reception – | Orange Ethernet |